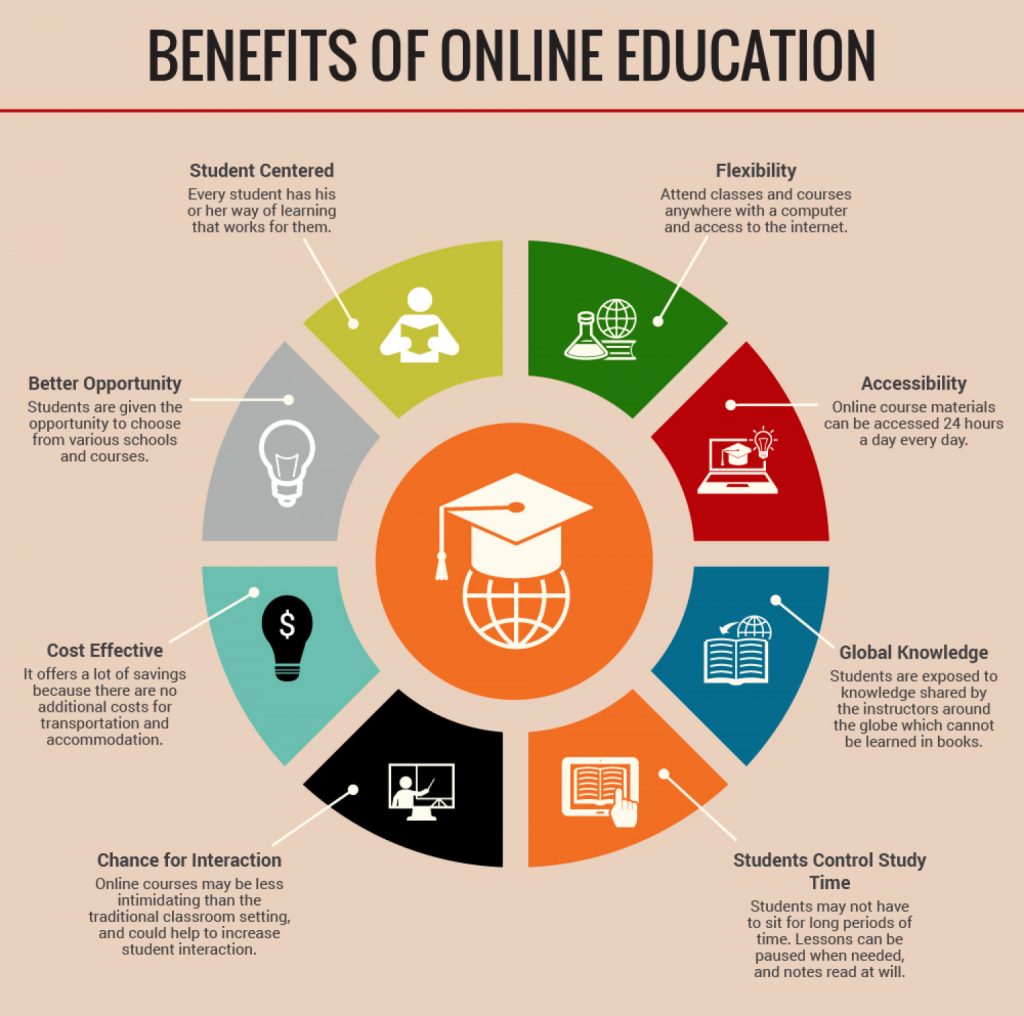
Benefits of M-Ecep
Benefits of M-ECEP program can be gained from 3 Pillars of the M-ECEP Program, the Partner Colleges and Universities, and the MSSAA Technology Corporation.
From the 3 Pillars of the M-ECEP Program
- Productive high school years for students while earning a high school diploma, college/university credits, and college/university education experiences.
- Refined career paths for students resulting in an aligned selection of colleges/universities for undergraduate studies.
- Significant savings for students and families on college/university tuition by the time of college/university completion.
- Opportunity for students and parents to select from a wide variety of Regionally Accredited Colleges/Universities Institutions across the United States before and/or during engagement of the M-ECEP program.

From the Partner Colleges and Universities
- Early Access to Partner University Curriculums: Students gain valuable exposure to college-level or university-level coursework aligned with their career aspirations.
- Guaranteed College Transcripts and Recommendations Letter: Even if students don’t pursue a transfer to a partner university, they can receive transcripts and recommendation letters that are widely recognized by major institutions.
- Dedicated Admission and Academic Support: Students have early access to dedicated and comprehensive admission and academic support from partner colleges and universities during and after graduating from the M-ECEP program
From the MSSAA Technology Corporation
- Strong Alumni Network: Students benefit from connections with the MSSAATech alumni network at all levels (high school, undergraduate, graduate, and industry professionals).
- MSSAATech Workforce: Students benefit from an internship, externship, mentoring, and MSSAATech sponsored program for Optional Practical Training (OPT) and H-1B post-university graduation
Comparative Global Curriculum Assessment
Cambridge (ICSCE, O-Levels, A-Levels), Advanced Placement (AP) International Baccalaureate (IB), Early College Education, and WASSCE are all well-established global curriculum programs and equivalents for high school students to M-ECEP to gain college credit.
M-ECEP versus other Global Curriculum Programs
The table below presents curriculum, traditional age range, school year, number of subjects, and exams in comparing M-ECEP to global curriculum programs.
Curriculum | Traditional Age Range | School Year | Number of subjects | Exams |
M-ECEP | 14-18 | Year 11-Year 13 | Minimum of 3 college and/or university courses | Exam taken at college or university |
Cambridge International GCSEs | 14-18 | Year 11-Year 13 | 4-5 (minimum) | External, offered 2-3 times a year |
Cambridge A Levels | 14-18 | Year 11-Year 13 | 4-5 (minimum) | External, offered 2-3 times a year |
Cambridge O Levels | 14-16 | Year 11-Year 12 | 4-5 (minimum) | External, offered 2-3 times a year |
International Baccalaureate (IB) | 16-18 | Year 12 – Year 13 | 6 subjects plus 3 papers | One cumulative external exam at the end of 2 years with some internal weightage |
Advanced Placement (AP) | 15-18 | Anytime in Grades 10-12 | Varies in addition to high school classes | External offered once a year |
WASSCE | 14-17 | Year 11-Year 13 | English, mathematics, integrated science, social studies, and three or four elective subjects | Offered by WAEC |
Background Information on M-ECEP Program and other Global Curriculum Programs
Advanced Placement (AP)
AP courses tend to focus heavily on content. AP tests are generally focused on multiple-choice questions, with a handful of open-response questions at the end. In general, even these open response questions focus on providing factual information, that conforms with the information provided in the course.
One advantage of the AP program is that students can choose the classes in which they want to take exams. This allows them to explore a wide range of subjects.
International Baccalaureate - IB
The IB program focuses on writing and broad thinking and is structured as a comprehensive diploma program. The goal of the IB program is to create adaptable people who can handle today’s difficulties. Students follow a more prescribed path through the IB program than AP or Cambridge, with fewer options of courses to choose from.
In terms of college admissions, U.S. college’s view both AP and IB courses as evidence of academic success. Both can earn you college credit. The main difference is that AP is more widely recognized in the U.S., while IB is more internationally focused. Thus, it may be more appealing to students considering attending a university outside of the United States.
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (IGCSE)
Cambridge offers this program to engage students. Courses provided a strong basis for achieving academic and personal success. The Cambridge curriculum focuses on the use of broad thinking and writing abilities and their growth and demonstration. The questions on Cambridge assessments are open-ended application questions that expose students to new structures they have never seen before.
IGCSE is a famous international qualification for fourteen to sixteen-year-olds. The university is recognized by leading universities and employers. IGCSE is equivalent to UK GCSE, O level, fifth form, or year eleven, respective to the student’s country and school. Its courses offer a variety of ways for learners with a wide range of abilities, including those whose first language is not English. After IGCSE, students can proceed to take Advanced Level (A-level or sixth form or year 12 and 13) or Pre-U (pre-university) studies.
Cambridge General Certificate of Education (GCE) Ordinary Level (O Levels)
The GCE system is a Cambridge program. Cambridge programs are carefully designed to engage students and give them a solid basis to achieve high levels of academic and personal success. The Cambridge courses focus on the development of broad thinking, writing and the application of those skills. Cambridge tests are primarily open-ended application questions, including exposure to novel situations students have not encountered before.
It is not directly equivalent to any educational qualification in the United States. However, some US universities may recognize GCE qualifications and accept them as part of their admission requirements.
The GCE “O” Level is equivalent to the US high school diploma, although the program is more precise than the high school diploma. This qualification is taken by students in the final year of their secondary education. It covers a wide range of subjects. It covers English, mathematics, science, humanities, and languages. The GCE “O” Level is equivalent to the General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) in the United Kingdom and other countries.
The GCE “O” Level is a broader-based qualification. It covers various subjects and is taken at the end of secondary education.
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (IGCSE)
Cambridge offers this program to engage students. Courses provided a strong basis for achieving academic and personal success. The Cambridge curriculum focuses on the use of broad thinking and writing abilities and their growth and demonstration. The questions on Cambridge assessments are open-ended application questions that expose students to new structures they have never seen before.
IGCSE is a famous international qualification for fourteen to sixteen-year-olds. The university is recognized by leading universities and employers. IGCSE is equivalent to UK GCSE, O level, fifth form, or year eleven, respective to the student’s country and school. Its courses offer a variety of ways for learners with a wide range of abilities, including those whose first language is not English. After IGCSE, students can proceed to take Advanced Level (A-level or sixth form or year 12 and 13) or Pre-U (pre-university) studies.
General Certificate of Education (GCE) Advanced Level (A Levels)
The GCE “A” Level is a Cambridge program. Cambridge programs are carefully designed to engage students and give them a solid basis to get high levels of academic and personal attainment. The Cambridge courses focus on the development and demonstration of broad thinking and writing. Cambridge tests are primarily open-ended application questions, including exposure to novel situations students have not encountered before.
In the US, it is equivalent to the US Advanced Placement program or the IB program. Therefore, it can be considered as up to one year of undergraduate study at an accredited institution of higher education. The GCE “A” Level qualification is taken after the completion of the “O” Level course at around 18 years of age. The “A” Level is a two-year course of study and offers a more in-depth study of a narrower range of subjects, often with a focus on preparing students for university study. “A” Level qualifications are highly valued by universities and employers and are considered a prerequisite for many higher education courses in the UK and other countries.
The GCE “A” Level offers a deeper study of fewer subjects. This program is taken by students who plan to attend university.
West African Senior Secondary Certificate Examination (WASSCE)
WASSCE is a test in West Africa. Students who pass the Exam get a certificate of graduation. The West African Examinations Council administers this program. It is only offered to candidates living in Anglophone West African countries. The academic school-leaving qualification awarded upon successful completion of the exams is the West African Senior School Certificate. The WASSCE tests four core subjects—English, mathematics, integrated science, social studies, and three or four elective subjects. The Examination is conducted twice a year, in May/June (for final-year students in senior secondary schools) and November/December (for secondary school leavers who want to correct deficiencies in their previous results).
The U.S. equivalence of WAEC is a high school diploma. In fact, to be accepted into an undergraduate program, U.S. universities generally take five WASSCE passes.
M-ECEP Program versus Early College Education Initiative (ECEI)
M-ECEP program allows students pursuing the WAASCE, IB, Cambridge, ISCE, and AP programs to earn at least nine transferable college credits from accredited US colleges and universities. The program ensures that students gain the rigor of both internationally recognized curriculum, early research experience, and early exposure to US college or university courses. The only academic responsibility outside the student’s high curriculum is college or university quizzes, exams, and projects.
M-ECEP Program is potentially a new program that is being started outside the United States. In the United States, the M-ECEP program aligns with the ECEI program started by the Gates Foundation in 2012. To date, it is the norm for interested families of high school students in the United States because of the numerous benefits below, which have been validated by the United States Education:
- The ECEI program allows eligible high school students to earn a minimum of 15 transferable college credits. This can be achieved while fulfilling the requirements for Advanced High School Diploma Studies. The result? A more productive senior year in high school and significant savings on college tuition costs.
- The ECEI program enables positive impacts of Early College Education on college enrollment and degree attainment, which is continued for at least 6 years after expected high school graduation.
- The ECEI program students have significantly higher rates of high school graduation, college enrollment, and college degree attainment than Early College students.
- The ECEI program per-student lifetime benefits of Early Colleges substantially exceeded the per-student cost.
- The ECEI program investment pays off with lasting benefits for students and the broader population.
Please review the benefits of the M-ECEP Program to understand the stated benefits highlighted for international student admission into the M-ECEP program.
Global Programs and M-ECEP - In the United States
Any student pursuing any of the recognized global curricula qualifies to engage in the M-ECEP. ECEP is already being executed for United States citizens interested in early learning by the ECEI. The M-ECEP is an extension of the ECEI to international high school students via partnered United States colleges and/or universities.
ECEP is already being executed for United States citizens interested in early learning.

